In today’s digital age, where cloud services are becoming increasingly prevalent, internet security has taken center stage. Cloud security, also known as cloud safety, has become a vital component in safeguarding the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data within cloud-based environments.
As more businesses and individuals rely on cloud infrastructure to store and manage sensitive information, the importance of addressing security concerns cannot be overstated.
This article delves into the critical role cloud security plays in the broader scope of cybersecurity, explores the challenges we face, and outlines key steps you can take to protect your data and systems in the cloud.
What is cloud server security?
Cloud security is a set of practices, technologies, policies, and controls designed to protect data, applications, and infrastructure stored and running in cloud environments.
In the context of cloud-based services such as data storage, computing, and software accessed over the Internet, cloud security aims to maintain the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information and prevent unauthorized access or potential cyber threats.
The main goal of cloud security is to keep data and systems in the cloud environment safe from various types of risks, including cyber attacks, data leaks, malware, and unauthorized access attempts.
To achieve this goal, various security measures are implemented, including data encryption, strong authentication and authorization, and monitoring for suspicious activity, in addition to implementing security incident response and response measures.
As cloud services grow and data migrates to these environments, cloud security becomes more important than ever.
Organizations and individuals must understand the risks associated with storing and managing data in the cloud and implement appropriate security practices to maintain the privacy and integrity of information.
Advantages and Benefits of Cloud Security
Cloud security offers several important benefits to individuals and organizations using cloud-based services.
1. Scalability and flexibility
One of the main advantages of cloud security is that you can easily scale and adapt your security requirements as the scope of your business changes.
This allows organizations to scale their security resources up or down as needed without making major investments in additional hardware or software.
2. Expert-based security
Large cloud providers typically have dedicated security teams that continuously monitor and manage security risks.
This means cloud users can benefit from the expertise and experience of security experts who dedicate their time to protecting their infrastructure and data.
3. Data encryption
Cloud security often provides strong data encryption options both in transit (i.e., when data is sent over a network) and at rest.
This helps prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information.
4. Continuous monitoring
Cloud security services often come with advanced monitoring tools to detect suspicious activity or cyber threats.
This allows you to respond quickly to security incidents and reduce their potential impact.
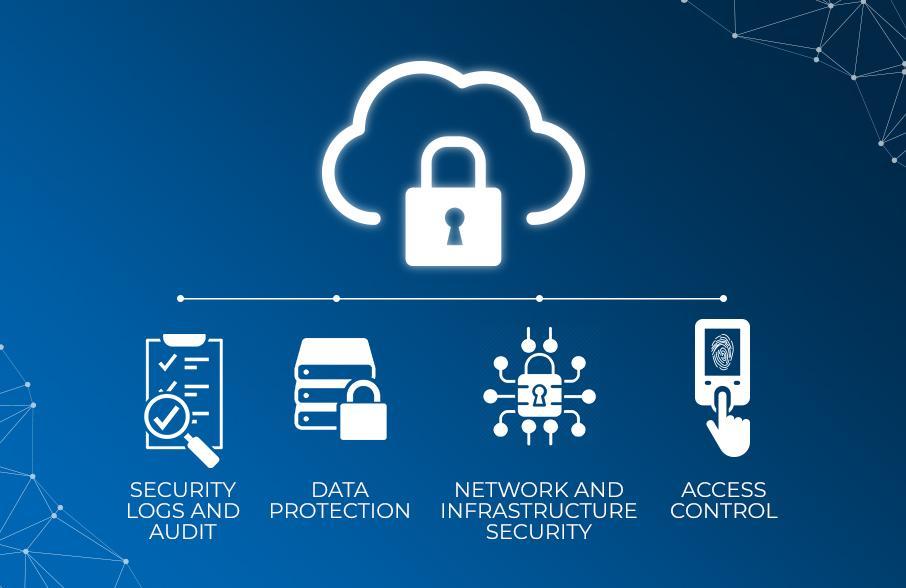
5. Access control
Cloud security enables tight access control. This means that only people with the appropriate permissions can access specific data and resources in your cloud environment.
The benefits of cloud security include:
6. Data protection
The biggest benefit of cloud security is protecting against the risk of data leaks or unauthorized access.
This is especially important if sensitive or confidential information is stored in a cloud environment.
7. Compliance and regulation
Cloud security helps organizations meet data security requirements set by specific regulations and industry standards.
This is especially important in areas where there is a legal obligation to keep data secure, such as finance and healthcare.
8. Availability and reliability
Proper cloud security ensures your data and applications remain available and functional even in the event of an incident or attack.
Integrated redundancy and disaster recovery ensure business continuity.
9. Operational efficiency
By relying on cloud service providers for security aspects, organizations can focus on their core operations without investing significant resources in managing security themselves.
10. Unlimited innovation
Strong cloud security enables organizations to execute new digital initiatives and experiences with more confidence without worrying too much about major security risks.
Overall, cloud security not only improves data and infrastructure security, but also enables you to use cloud services more efficiently and productively.
How cloud server security works
How cloud security works involves multiple layers of protection and security practices designed to protect data and infrastructure in a cloud environment. Here are some common steps taken in cloud security:
1. Data encryption
Encryption is a key method of cloud security. Data transmitted or stored in the cloud is encrypted. This means that the data is converted into a format that can only be understood by those who have the appropriate decryption key.
This helps prevent unauthorized access to data while it is being transmitted over the network and while it is being stored.
2. Identification and licensing
High security includes the use of strong authentication and authorization mechanisms. This means that users must prove their identity through processes such as passwords, two-factor authentication, or biometrics before accessing data or resources.
3. Activity monitoring
Cloud security systems are often equipped with sophisticated monitoring tools. This helps us detect suspicious or unusual activity, such as unauthorized access attempts or unauthorized data changes.
Active monitoring helps identify potential threats before they cause more damage.
4. Firewall and network protection
Implementing firewall and network protection solutions aims to prevent unauthorized access and prevent attacks from accessing systems and data.
This also includes the use of intrusion detection technology that can detect suspicious activity or signs of an attack in progress.
5. Disaster recovery
Cloud security includes a disaster recovery plan that allows you to recover data and systems in the event of a major incident or power outage.
Regular data backup and a proven recovery strategy are critical to maintaining business continuity.
6. Data classification and access control
Data is often classified based on its sensitivity level, and access controls are applied based on this classification.
This ensures that only authorized individuals have access to sensitive data.
7. Updates and fixes
Systems and software used in cloud environments must always be updated with the latest security patches.
This helps protect your system from vulnerabilities that can be exploited by attackers.
8. Security training and awareness
Users and staff involved in managing cloud environments must be trained in appropriate security practices.
When it comes to cloud security, awareness of cyber threats and the steps you can take to mitigate risk is critical.
9. Risk assessment
Ongoing risk assessment is critical to identifying potential new threats and adapting security strategies as the technology and threat landscape changes.
10. Accident management
When a security incident occurs, you need to respond quickly.
This includes isolating and cleaning up attacks, as well as root cause analysis to prevent future attacks from recurring.
In general, cloud security involves a comprehensive approach to protecting data, applications, and infrastructure in a cloud environment from various cyber threats and other security risks.
Cloud security implementation cases
Here are some compelling examples of cloud security in action:
- Data Encryption
Many companies rely on cloud storage to safeguard sensitive customer information. End-to-end encryption ensures that data is encrypted before transmission and remains encrypted while stored in the cloud. Only those with the decryption key can access the data, keeping it safe even if intercepted by unauthorized parties during transit or storage.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
E-commerce platforms enhance account security with two-factor authentication (2FA). Beyond a password, users must also enter a unique code generated by an authenticator app on their mobile device. This additional security layer ensures that only users with physical access to the authentication device can successfully log in.
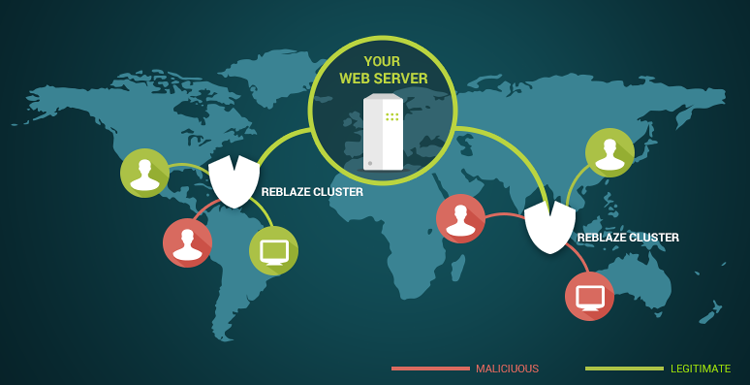
- Web Application Firewall (WAF)
Businesses that run critical web applications use web application firewalls (WAFs) to defend against attacks like SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS). WAFs monitor web traffic, detect malicious patterns, and block threats before they can reach the application, providing an essential security shield.
- Real-Time Security Monitoring
Cloud service providers utilize advanced monitoring systems to continuously track network activity. Any suspicious behavior, such as unauthorized access attempts or system intrusions, triggers an immediate response from a dedicated security team to investigate and mitigate the threat.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Large organizations manage access to cloud resources through Identity and Access Management (IAM) solutions. By assigning precise permissions based on an individual’s role, they ensure only authorized users can access specific data and applications, enhancing control over sensitive information.
- Disaster Recovery
E-commerce companies integrate cloud-based disaster recovery plans. In the event of an outage—whether due to natural disasters or cyberattacks—the ability to swiftly restore websites and data from cloud backups minimizes downtime and ensures business continuity.
- Regular Security Updates
Tech startups operating in cloud environments prioritize regular updates and security patches for their systems and software. By staying current with the latest security patches, they reduce the risk of exploitation from known vulnerabilities.
- Security Training
Financial institutions invest in cybersecurity training for all employees. This training covers common cyber threats, social engineering tactics, and essential security practices, fostering a culture of awareness and collective responsibility for maintaining security.
- Penetration Testing
Cloud service providers conduct regular penetration tests to uncover potential vulnerabilities. Independent security researchers simulate attacks to identify weak points that hackers might exploit, ensuring systems are fortified against future threats.
- Incident Response
E-commerce companies maintain robust incident response plans to quickly handle security breaches or attacks. These plans outline steps to contain the breach, clean compromised systems, notify authorities, and inform affected customers, helping to mitigate damage and restore trust.
Each organization’s cloud security strategy must be tailored to its unique needs and environment. The examples above highlight some of the most common and effective ways cloud security is applied to safeguard data and infrastructure in the cloud.